Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Seki, Akiyuki; Yoshikawa, Masanori; Nishinomiya, Ryota*; Okita, Shoichiro; Takaya, Shigeru; Yan, X.
Nuclear Technology, 12 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)Two types of deep neural network (DNN) systems have been constructed with the intent to assist safety operation of a nuclear power plant. One is a surrogate system (SS) that can estimate physical quantities of a nuclear power plant in a computational time of several orders less than a physical simulation model. The other is an abnormal situation identification system (ASIS) that can estimate the state of the disturbance causing an anomaly from physical quantities of a nuclear power plant. Both systems are trained and tested using data obtained from the analytical code for incore and plant dynamics (ACCORD), which reproduces the steady and dynamic behavior of the actual high Temperature engineering test reactor (HTTR) under various scenarios. The DNN models are built by adjusting, the main hyperparameters. Through these procedures, these systems are shown able to perform with a high degree of accuracy.
 Co radiation source under an intense
Co radiation source under an intense  Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr
Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields
spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.983 - 992, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishida, Shinya; Fukano, Yoshitaka
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 88(911), p.21-00304_1 - 21-00304_11, 2022/07
In previous studies, the reliability and validity of the SAS4A code was enhanced by applying Phenomena Identification and Ranking Table (PIRT) approach to the Unprotected Loss of Flow (ULOF). SAS4A code has been developed to analyze the early stage of Core Disruptive Accident (CDA), which is named Initiating Phase (IP). In this study, PIRT approach was applied to Unprotected Transient over Power (UTOP), which was one of the most important and typical events in CDA as well as ULOF. The phenomena were identified by the investigation of UTOP event progression and physical phenomena relating to UTOP were ranked. 8 key phenomena were identified and the differences in ranking between UTOP and ULOF were clarified. The code validation matrix was completed and an SAS4A model, which was not validated in ULOF, was identified and validated. SAS4A code became applicable to various scenarios by using PIRT approach to UTOP and the reliability and validity of SAS4A code were significantly enhanced.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Demachi, Kazuyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(5), p.559 - 567, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Facility design of nuclear power plant for a sabotage protection is investigated and an effect of the design change for damage control on reduction of sabotage risk is shown using the vital area identification methodology. The loss of offsite power leading to the station blackout is assumed to be a typical example for further evaluation. In this study, the vulnerability of target set is defined as the multiplication of the accessibility, the distribution of target and the degree of adversary's interference. The built-in measures for damage control are of vital importance in case of the existence of adversary's interference until neutralization. It is confirmed that not only the physical protection system but also the facility design play an important role in the effective and efficient sabotage protection. It is very important to introduce a security by design approach in an initial stage of the NPP construction while considering the interface between safety and security.
 Cs/
Cs/ Cs in the environment to identify the reactor units that caused atmospheric releases during the Fukushima Daiichi accident
Cs in the environment to identify the reactor units that caused atmospheric releases during the Fukushima Daiichi accidentChino, Masamichi; Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Katata, Genki; Mikami, Satoshi; Torii, Tatsuo; Saito, Kimiaki; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.31376_1 - 31376_14, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:98.61(Multidisciplinary Sciences) resolution
resolutionChatake, Toshiyuki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Tsyba, I.*; Bau, R.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 60(8), p.1364 - 1373, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.87(Biochemical Research Methods)A neutron diffraction study has been carried out at 1.6  resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from
resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from 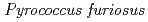 using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from
using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from 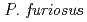 , the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS
, the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6
redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6  resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Yamagishi, Hideshi; Masaoka, Sei; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.336 - 341, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)A microstrip gas chamber (MSGC) with a capability of track discrimination for neutron detection was developed whilst ensuring the stability of the MSGC and fulfilling the specifications required for detectors using in high-flux reactors and high-intensity pulsed-neutron sources. The developed two-dimensional detector system comprises a MSGC with individual signal channel read-outs and a new instrument system with a capability of secondary-particle discrimination (InSPaD). The InSPaD identifies the particles -proton and triton- created in the nuclear reaction 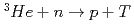 by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as
by a simple, fast and cost-effective method using the difference in the track length, and it enables a small amount of heavy gas such as 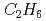 with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
with helium-3 to be used as the filling gas whilst achieving a high spatial resolution.
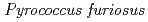 by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromolecules
by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromoleculesKurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Moiseeva, N.*; Bau, R.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(31), p.11215 - 11220, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:61.07(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The structure of a rubredoxin (Rd) from 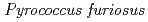 , an organism that grows optimally at 100
, an organism that grows optimally at 100  C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5
C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5  , and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of
, and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of  = 18.6 % and
= 18.6 % and 
 = 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
= 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
 terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
Tachibana, Mitsuo; Ito, Hirokuni*; Hatakeyama, Mutsuo*; Yanagihara, Satoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(1), p.120 - 127, 2004/03
The RAPID-1600 was developed to measure a low-level radioactive contamination on building surfaces automatically. The double layered detectors are structured by two gas flow type detectors with a  rays shielding plate between the two detectors and it is horizontally positioned. The lower counter measures
rays shielding plate between the two detectors and it is horizontally positioned. The lower counter measures  and
and  rays and the upper counter measures
rays and the upper counter measures  rays. The
rays. The  rays counting rates are derived by subtracting
rays counting rates are derived by subtracting  rays counting rates of the upper counter from
rays counting rates of the upper counter from  and
and  rays counting rates of the lower counter. This mechanism results in sensitive to
rays counting rates of the lower counter. This mechanism results in sensitive to  rays against to low background radiation conditions. The driving unit can move omnidirectionally by controlling two driving wheels individually, and has a capability to correct its position if an orbital error is detected by the self-position identification system. The RAPID-1600 was successfully applied to the actual measurement in the radioisotope production facilities. The RAPID-1600 is expected to be a useful tool for measurement of radioactivity in decommissioning nuclear facilities.
rays against to low background radiation conditions. The driving unit can move omnidirectionally by controlling two driving wheels individually, and has a capability to correct its position if an orbital error is detected by the self-position identification system. The RAPID-1600 was successfully applied to the actual measurement in the radioisotope production facilities. The RAPID-1600 is expected to be a useful tool for measurement of radioactivity in decommissioning nuclear facilities.
Ono, Tomio*; Subekti, M.*; Maruyama, Yuta*; Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Kudo, Kazuhiko*
Dai-13-Kai Interijento, Shisutemu, Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.212 - 217, 2003/12
In this research, we present nuclear power plant simulation method using Multilayer Perceptron, which is one of the models of Artificial Neural Networks(ANNs). The major characteristics of ANNs are to obtain the model through learning, analogy and very high speed processing. Furthermore, 'time synchronizing signal' and 'progress synchronizing signal' are added as the inputs to adapt the abnormal events with various scales or progress rates. This ANN, learned some sample data, can be flexibly adapted to simulate the abnormal events with different scales including explicit progress rates. In the verification using PWR simulator, we confirmed that this method could model NPP abnormal events by learning data and simulate the data which have different progress rates from learning data.
Yanagihara, Satoshi; Hatakeyama, Mutsuo; Ito, Hirokuni; Mori, Shunji*; Takagi, Akira*
Advanced Robotics, 15(3), p.293 - 300, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.29(Robotics)Automatic measurement of building surface radioactivity must be a useful approach for decommissioning and maintenance activities in nuclear facilities. In particular, in the final step of decommissioning a nuclear power plant, it is essential to confirm that there is no effective radioactivity on building surfaces by measurement. However, experience showed that hands-on measurement using conventional detectors requires a great deal of labor-hours for all building surfaces in relatively large facilities. To realize the automatic measurement of building surface radioactivity, a mobile robot equipped with highly sensitive surface detectors has been developed; it can move automatically based on route plans to measure radioactivity on concrete floors and walls. In the development of this system, efforts were especially made to realize accurate robot motions by applying self-position identification system in consideration of the fact that the measurement should cover all the surfaces of planned areas with minimum overlap.
Ebihara, Kenichi
JAERI-Tech 95-012, 53 Pages, 1995/03
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Toyoaki; Kawamata, Yoichi; *
Fusion Technology 1994, 0, p.691 - 694, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
*; ; ;
JAERI-M 9514, 20 Pages, 1981/06
no abstracts in English
; *; ; ;
JAERI-M 9175, 161 Pages, 1980/12
no abstracts in English
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 17(10), p.737 - 746, 1980/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; *
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 18(7), p.408 - 414, 1976/07
no abstracts in English
; ; ;
JAERI-M 6252, 104 Pages, 1975/10
no abstracts in English
Seki, Akiyuki; Yoshikawa, Masanori; Okita, Shoichiro; Takaya, Shigeru; Yan, X.
no journal, ,